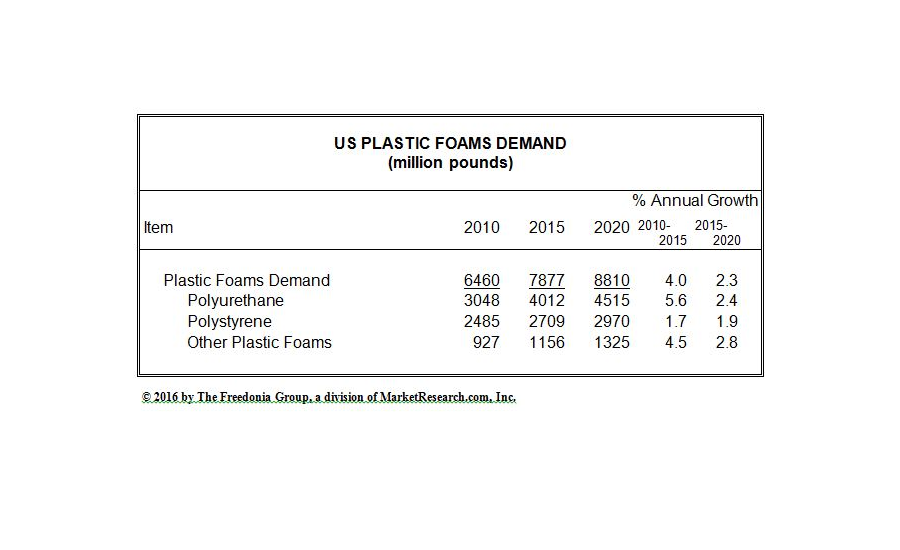
U.S. demand for plastic foams is forecast to rise 2.3% annually to 8.8 billion pounds in 2020, valued at $25.2 billion. Growth will decelerate from the rate posted during the 2010-2015 period. The construction sector is anticipated to lead growth prospects, due to additional opportunities for foam insulation products bolstered by increasing construction activity. Rising consumer spending levels will bode well for foams used in household products such as bedding, furniture, and appliances. In the motor vehicle market, advances will slow in tandem with slowing motor vehicle production and by trends favoring smaller, more fuel efficient automobiles that require less foam on a per vehicle basis. These and other trends are presented in Plastic Foams, a new study from The Freedonia Group (freedoniagroup.com), a Cleveland-based industry research firm.
Polyurethane represents the leading resin in the plastic foams market. Rigid polyurethane foam will remain the dominant product type. Demand gains through 2020 will be based on growth in construction activity and by changes in building codes and construction practices calling for more energy efficiency. Rigid polyurethane is one of the most effective materials available for roof and wall insulation, insulated windows and doors, and air barrier sealants. However, polyurethane foam insulation will continue to face competition from fiberglass and polystyrene foam, which are lower cost alternatives. Flexible polyurethane foam will remain in high demand through 2020 based on healthy growth in the bedding and carpet underlay markets, where it is valued for its cushioning properties.
Polystyrene accounted for over one-third of demand for plastic foam in 2015 and will maintain a sizable share of the market based on its excellent protective and insulative capabilities, moisture resistance, and low cost. However, advances in the large packaging sector will be restrained by ongoing solid waste disposal concerns regarding the use of disposable foam products and rising competition from paper-based materials, which are viewed as more eco-friendly. Through 2020, expanded polystyrene foam is projected to see more rapid gains than its extruded counterpart, stemming primarily from its use in insulation, molded foam protective packaging, and insulated shipping containers. Expanded polystyrene geofoam, which serves as a cost-efficient and lightweight alternative to traditional fill materials in construction applications, is predicted to exhibit especially rapid growth, albeit from a relatively small base.