We’ve seen many innovations related to the service, production, packaging and distribution of food over the years. These changes all aim to protect public health and create a more efficient and sustainable food industry. The following are ways that one innovation, artificial intelligence (AI), is helping the food industry to achieve its goals.
1. Decision Making
In previous years, certain smart technologies could be considered as AI, such as Expert System, Machine Learning, Fuzzy Logic (FL) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Fuzzy logic has been previously used in manufacturing industries such as coffee roasting. In recent studies, FL was used to create an intuitive system that enabled the consistent roasting of coffee beans — even when there were great variations on bean characteristics (e,g, weight and the presence of minor or major defects.). Systems such as these reduced the need for intervention from an expert to aid processing when different materials arrived.
On the other hand, ANN is a smart technology that was designed to mimic the way a human brain works when making a decision. This system has been used to intuitively solve food processing problems even with non-linear patterns. It is used to predict the effects of varying conditions on the yield and characteristics of products.
Together, ANN and FL are combined to create a more logical system called Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interface System (ANFIS). ANFIS takes some of the best features of FL and ANN in an attempt to go even further and automate the decision-making process. Through this integration, systems can create more accurate and trustworthy decisions in food processing. Such innovations can also be used to improve energy efficiency during production without the need for expert assistance.
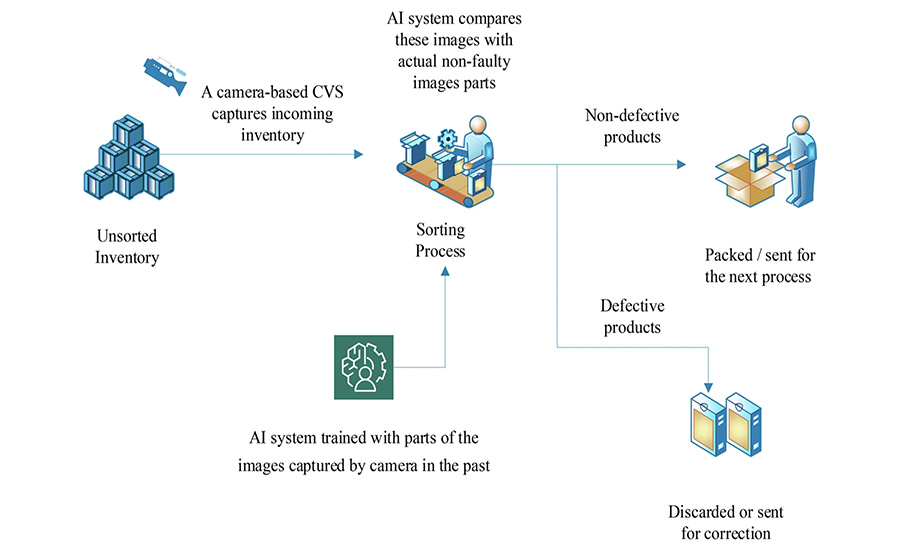
2. Detection and External Sensors
You may have heard about the use of AI in automated scanning for physical defects, but have you heard about it being used in detecting other sensory cues such as smell and taste? The systems of AI have been integrated into machines that can sense odors and flavors intuitively for the control of food safety and quality as well as deep analysis of product composition. In such innovations, features used in the extraction and recognition of patterns are used to come up with resulting details. Sensors are used to extract the marker components, and intelligent algorithms translate the elicited signals to come up with the information needed.
This innovation removes the need for food handlers to conduct the sensory analysis themselves, which can negatively affect their health. In addition, the use of AI in the selection and analysis of food components and characteristics — as well as in the detection of defects — ensures a more uniform approach while reducing the possibility of errors.
3. Food Safety Management
On a more business-centric point, AI Innovations have also significantly contributed to improving food safety management. Food companies have adapted to the shift in focus of food agencies toward proactively addressing food-safety hazards. Businesses have started to use automated monitoring procedures and have become less dependent purely on human resources. This type of innovation is seen in FoodDocs, a company that offers an automatically generated food-safety management system (FSMS) based on the nature of participating food businesses.
This company generates a digital food-safety management system for all types of food businesses. The process only involves answering a few basic questions about the food business, and the digital FSMS can be completed within 15 minutes. The company uses a machine-learning program to suggest the most relevant monitoring procedures, forms and tools based on the food owner’s specifications of its operations. Additionally, the system switches all monitoring procedures to a digital platform and allows food safety managers to review their everyday progress using a real-time dashboard. The report generated from this system highlights the food-safety areas that need extra attention.
Artificial intelligence has propelled the food industry to greater lengths. With less human intervention, the percent damages and errors from unpredictable human behavior are minimized. The advances in terms of service, preparation and management of food operations makes life even easier for food business owners, operators and consumers alike. The future is looking even more promising as food companies and technology innovators strive to satisfy consumers while keeping them healthy in the most efficient way possible.

